Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors account for 10% of all brain tumors. It has not been fully elucidated how tumors, most of which are benign, form. A few of them are genetically inherited.
What are the Symptoms of a Pituitary Tumor?
Tumors that form in the pituitary gland can present with a wide variety of symptoms, including headache, menstrual irregularity, weight gain, hair loss, visual impairment, and blood pressure changes. At this point, the size of the tumor, its location, and the type and amount of the hormone secreted more than normal are important.
Headache, which is the most common symptom related to tumors, has no typical features. Pituitary gland tumors should be considered in chronic headaches that do not go away despite treatment.
Another important finding of pituitary tumors is visual impairment. As the tumor grows and affects the optic nerves, symptoms such as narrowing of the visual field, double vision, or droopy eyelids may occur over time. The most common visual impairment is narrowing of the visual field (in this case, the patient sees as if he/she is looking through a pipe and cannot see around). The drooping of the eyelid that cannot be explained by other reasons should suggest a pituitary gland enlarged to the sides. Therefore, the possibility of a pituitary tumor should be considered in case of visual impairment. Bleeding into the pituitary gland may lead to an emergency picture and delay in treatment may be the cause of death.
How Is Pituitary Tumor Treated?
An endocrinologist should make a definitive diagnosis of the disease. According to the clinical picture, medication, surgery, and radiation therapy can be applied. If excessive hormone secretion and tumor growth cannot be stopped by medical or surgical treatment, radiation therapy can be applied. Surgical treatment is in the first place in an important part of pituitary tumors. It may be possible to completely get rid of the disease with an expert and experienced surgical team and sufficient technological infrastructure. However, nowadays, medication therapy is becoming increasingly common in parallel with the successful results obtained and can sometimes be the first treatment.
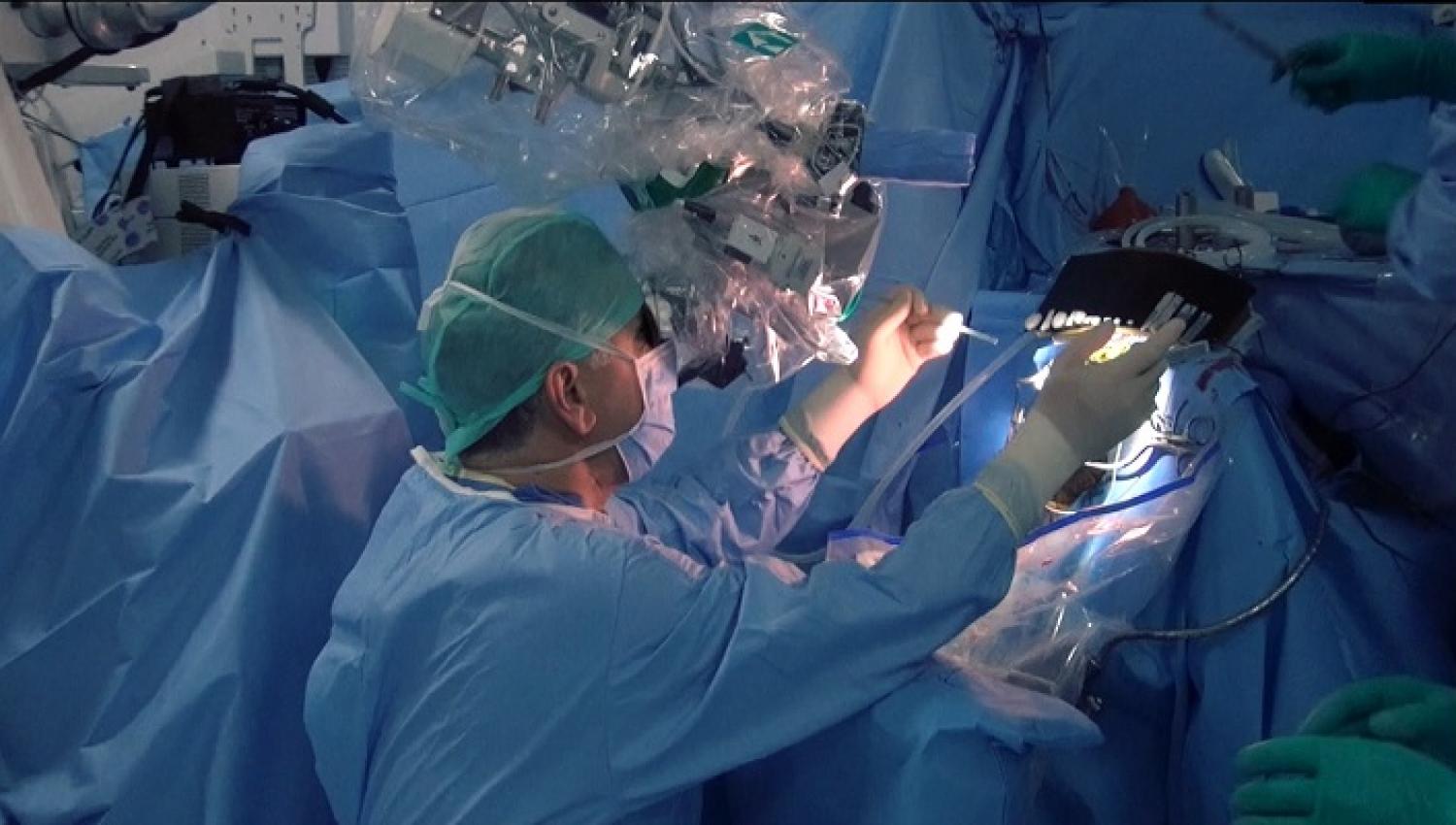
Surgical Treatment of Pituitary Diseases
Surgical treatment is the first place in a significant part of pituitary tumors. It is possible to completely get rid of the disease with an expert and experienced surgical team and sufficient technological infrastructure. During the preparation for surgery, a laboratory with the capacity to perform detailed radiological imaging (3-Tesla MR, CT, etc.) and hormone tests, and evaluation of the patients by a team consisting of neuro-ophthalmologists, neuro-radiologists, endocrinologists, and anesthesiologists who will examine the preoperative condition of the patients in detail constitute the most important step.
Purposes of Surgical Treatment
- Determining the histopathological diagnosis of the lesion
- Removing the pressure effect in the surrounding important tissues (the nerves responsible for the vision and eye movements)
- Removing the entire lesion where possible
- Preserving normal pituitary tissue
- Providing relief of symptoms before surgery
Surgical Treatment Options in Pituitary Diseases
The methods commonly used in the surgical treatment of pituitary lesions are as follows:
Transsphenoidal Surgery
Under general anesthesia, it is reaching the pituitary lesions by opening a bone window in the skull base by entering through the nose and removing the lesions with the help of a microscope or an endoscope. This type of surgery is widely used and is mostly preferred for small lesions. Other surgical treatment options are evaluated in areas that are difficult to reach with transsphenoidal surgery or may be risky with transsphenoidal surgery.
Transcranial Surgery
It is reaching the lesion by opening a bone window in the skull and removing the lesion with the help of a microscope. Craniotomy surgery is preferred especially in large lesions and lesions that cannot be reached completely by the transsphenoidal route.
While determining the type of surgery, it is decided by evaluating many factors such as the size of the lesion, its relationship with the surrounding tissues, the type of the lesion, and the physical structure of the patient (nasal anatomical structure). All methods can be successfully applied by experienced surgeons at Yeditepe University Koşuyolu Hospital.
Factors Affecting the Success of Surgical Treatment in Pituitary Tumors
- Experience of the surgical team,
- Having sufficient technological infrastructure,
- Having advanced technology imaging devices (3-Tesla MR, CT, HD Neuroendoscope, Intraoperative MRI, Neuronavigation, Intraoperative Ultrasound),
- Operating rooms equipped with advanced technology (Intraoperative MRI, Intraoperative Ultrasound, Neuronavigation, HD Neuroendoscope),
The patient is evaluated in detail by a team consisting of endocrinologists, neuro-radiologists, neuro-pathologists, neuro-ophthalmologists, radiation oncologists, and anesthesiologists before the surgery.
In Which Patients Should Surgery Be Considered in the Foreground?
- Pituitary Apoplexy = Sudden bleeding in pituitary tumors,
- Large tumors that cause pressure on the optic nerve and cause vision problems in the patient,
- Cases that affect the hormonal balance and functioning of the body by secreting excessive hormones and do not respond to medication therapy,
- Recurrent cases after surgery,
- Cases that cannot be diagnosed despite all examinations and analyses,
- Cases resistant to medication therapy.
”